Blog NIST CSF 2.0: What’s New
NIST CSF 2.0: What’s New
Established in 2014, the National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF) is a vital tool in the field of cybersecurity. The framework’s effectiveness in addressing these risks is well recognized, with many organizations affirming the efficacy of the previous version, NIST CSF 1.1.
However, with the ever-evolving nature of cybersecurity threats, there is a consensus that updates are necessary to tackle current and future challenges. This has led to the development of the NIST CSF 2.0, aiming to enhance the framework while preserving its original goals and objectives.
With this updated version, NIST strives to streamline the framework’s application, making it even more accessible and effective for organizations. NIST CSF 2.0 signals a significant step forward in cybersecurity management, promising to equip businesses with the necessary tools to navigate the increasingly complex cyber landscape.
Understanding NIST CSF 2.0
NIST CSF 2.0 comes as a response to the significant changes in the cybersecurity landscape over the past decade. These shifts include:
- The evolution of cyber threats, such as the surge of multi-extortion ransomware and the growing prevalence of attacks utilizing advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and automation.
- Advances in cybersecurity capabilities, including zero-trust capabilities, automation to combat cyberattacks, and secure software development.
- Changes in the workforce, notably the global shortage of cybersecurity professionals.
- Technological advancements, like the evolution of cloud services and deployment models with associated security risks and the progression of AI, machine learning, quantum computing, and encryption.
- Increased availability of resources to aid organizations in managing their cybersecurity risk.
Despite these extensive updates, CSF 2.0 retains the original framework’s essential elements. It remains voluntary for the private sector, maintains a risk-based approach to cybersecurity, focusing on desired outcomes rather than specific controls, and retains the structure of the CSF, consisting of three main components:
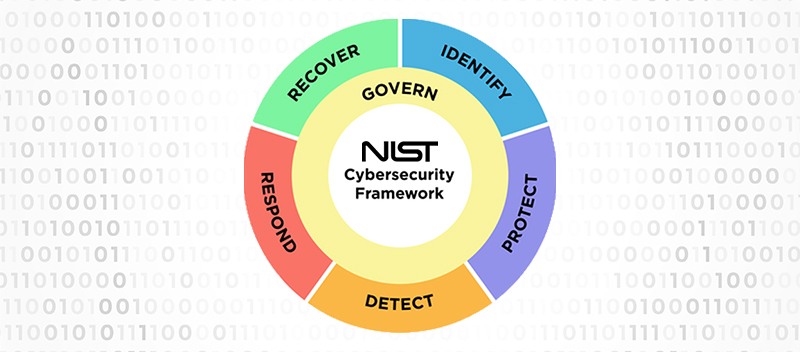
- Core: The core of CSF organizes desired cybersecurity outcomes around five functions: identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover. CSF 2.0 introduces a sixth function: govern. These functions are the pillars of effective cybersecurity7.
- Tiers: The tiers of CSF describe how an organization manages its cybersecurity risk. Organizations select the tier that aligns with their goals, reduces cyber risk to an acceptable level, and is feasible to implement. Progressing from tier 1 to tier 4 signifies increasing sophistication in cyber risk management processes.
- Profiles: CSF profiles assist organizations in establishing a roadmap for reducing cybersecurity risk. They depict an organization’s current and target cybersecurity posture, guiding organizations in their progression from one stage to another.
In essence, NIST CSF 2.0 is not a departure from its predecessor but rather an evolution, considering the changing cyber landscape and equipping organizations with the tools they need to navigate these changes effectively.
Learn more about our cybersecurity and compliance services Here
Key Features of NIST CSF 2.0
NIST CSF 2.0 introduces several new features and improvements that reflect the changes in the cybersecurity landscape. Here are the key features:
Expanded Scope: CSF 2.0 broadens its reach beyond critical infrastructure organizations, for which the original framework was designed, to include organizations of all sizes and sectors, including small businesses. This change acknowledges the widespread adoption of the CSF beyond critical infrastructure organizations and aligns with Congress’s directive for NIST to consider the needs of small businesses within the framework.
Governance: Recognizing the drastic changes in the cyber landscape over the past decade, CSF 2.0 elevates the importance of governance. It identifies cyber risk as a significant source of enterprise risk that requires the attention of senior leadership, on par with legal, financial, and other sources of enterprise risk.
Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM): CSF 2.0 acknowledges the cybersecurity risks associated with external parties or supply chains. Standard supply chain cyber risks include malware attacks, ransomware attacks, data breaches, and cybersecurity breaches.
Zero-Trust Architectures (ZTA): CSF 2.0 embraces the zero-trust security model, an alternative to the traditional perimeter security model. The zero-trust model takes a “never trust, always verify” approach to security, a key element in establishing cybersecurity for the federal government.
Cloud Security: CSF 2.0 recognizes the shift in cloud security from organizations managing their cloud infrastructure to third-party companies taking legal and operational responsibility for managing the cloud.
Expanded Implementation Guidance: To assist organizations in achieving the cybersecurity outcomes outlined in the framework, CSF 2.0 provides expanded “implementation examples” and “informative references.”
The enhancements introduced in NIST CSF 2.0 are a testament to its evolution with the changing cybersecurity landscape.
Impact of NIST CSF 2.0 on Cybersecurity
The NIST CSF 2.0 has introduced significant changes to the cybersecurity landscape. Its expanded scope and emphasis on governance empower organizations to improve their cybersecurity posture and reduce the risk of cyberattacks. The updated framework provides structure, standardization, and consistency in addressing cyber risks, aiding enterprises to increase compliance and manage their cyber risk effectively.
Furthermore, the inclusion of Zero-Trust Architectures (ZTA) principles and focus on cloud security exhibit a proactive approach towards managing cybersecurity, enabling organizations to anticipate and mitigate threats.
In real-world applications, NIST CSF 2.0 will impact Managed Service Providers (MSPs) and Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs). They may leverage the framework’s strategies to manage cybersecurity posture better and reduce risks.
Additionally, its influence extends to sectors like healthcare, where understanding and implementing the new features of NIST CSF 2.0 can significantly enhance security measures. Also, the Third Party Risk Management (TPRM) programs benefit from determining priorities and risk tolerances and assessing cybersecurity risks and impacts.
In essence, NIST CSF 2.0 is instrumental in driving a more resilient and secure digital ecosystem.
Implementing NIST CSF 2.0
Implementing the updates in NIST CSF 2.0 can significantly enhance an organization’s cybersecurity posture. The first step involves understanding the CSF, its components, and its principles. Organizations must thoroughly assess their cybersecurity posture, identify gaps, and develop a measurable plan for implementing the CSF.
NIST aims to tackle a persistent issue that impedes the implementation of the CSF. The organization’s goal for the final 2.0 draft is to incorporate examples of implementation guidance that provide practical, real-world illustrations of how the framework can be applied.
While the current 2.0 draft does not include these examples, NIST has separately published samples of the guidance that might be featured in the final version, seeking public feedback. They have invited stakeholders to share their opinions on the specificity of these examples, the usefulness of other potential models, the frequency of updates, and other potential sources of implementation guidance that could serve as examples.
Ultimately, it’s important to remember that achieving optimal cybersecurity requires continuity. Continual assessment and improvement are necessary to adapt to evolving cyber threats. Therefore, organizations should maintain regular reviews and updates of their cybersecurity measures to remain effective.
Harnessing the Power of NIST CSF 2.0
NIST CSF 2.0 is a significant step forward in cybersecurity, offering features that support a comprehensive, robust, and adaptable approach to managing cyber risks. Keeping pace with the latest cybersecurity standards, such as the NIST CSF 2.0, is crucial in today’s digital landscape. It helps businesses protect their valuable assets, maintain stakeholders’ trust, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Implementing NIST CSF 2.0 is not just about enhancing your cybersecurity posture; it’s about securing your future.
Contact TrustNet today to further explore how NIST CSF 2.0 can strengthen your cybersecurity strategy.




